Rapid response through the simple and quick method diagnosis,
minimizing the economic loss of customers.
LIVESTOCK ANIMALS
RIDX®
IBDV Ag SP Test Kit
[LGM-YFG-11]
DESCRIPTION
Infectious bursal disease (IBD), also known as Gumboro disease, caused by Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) infection, is a highly contagious disease of young chickens characterized by immunosuppression and variable mortality. First identified in Gumboro, Delaware, in 1962, IBDV remains one of the most economically significant pathogens in the global poultry industry.
The RIDX® IBDV Ag Test Kit is a lateral flow chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of IBDV in poultry. This kit shows two letters which are the test (T) line and the control (C) line on the surface of the device. If the IBDV antigen exists in the sample, it binds to the gold-conjugated anti-IBDV antibody. The antigen-antibody complex moves through the membrane by capillary force and responds to the secondary anti-IBDV antibody on the test line, resulting in a red line. The control line indicates that the test is performed correctly and should appear when the test is complete.
Very specific monoclonal antibody to the VP2 protein, a major host protective immunogen of IBDV, are used as a capture and detector in the kit. The RIDX® IBDV Ag Test Kit can detect IBDV in poultry tissue (bursa of Fabricius) homogenate or cloacal swabs with high accuracy.
SPECIMEN
Avian bursa of Fabricius or cloaca
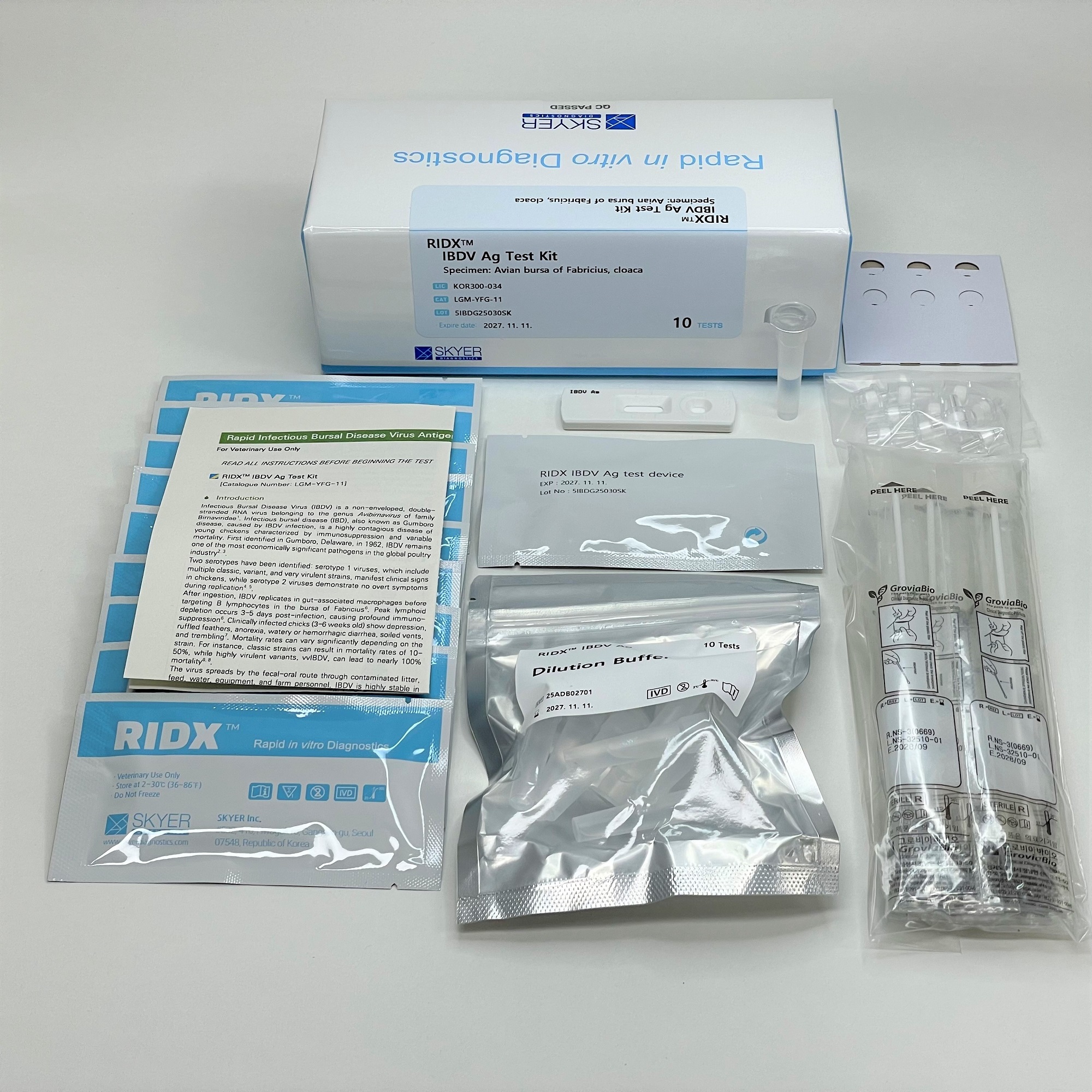
COMPONENTS
• RIDX IBDV Ag test device (10 tests)
• Sample dilution buffer (10 tubes)
• Disposable swab (10 ea)
• Dropper cap with filter (10 ea)
• Paper rack for standing buffer tubes (1 ea)
• Instructions for use (1 sheet)
FEATURES
• Sensitivity: 92.31% (12/13) vs. RT-PCR
• Specificity: 100% (15/15) vs. RT-PCR
• Diagnostic Agreement: 96.43% (27/28) vs. RT-PCR
• Limits of Detection: 1x105.8 EID50/mL
• No cross-reactivity with other avian pathogens (AIV, IBV, NDV, Mycoplasma gallisepticum, and Mycoplasma synoviae)
PACKAGE
• 10 Tests/Kit [LGM-YFG-11]
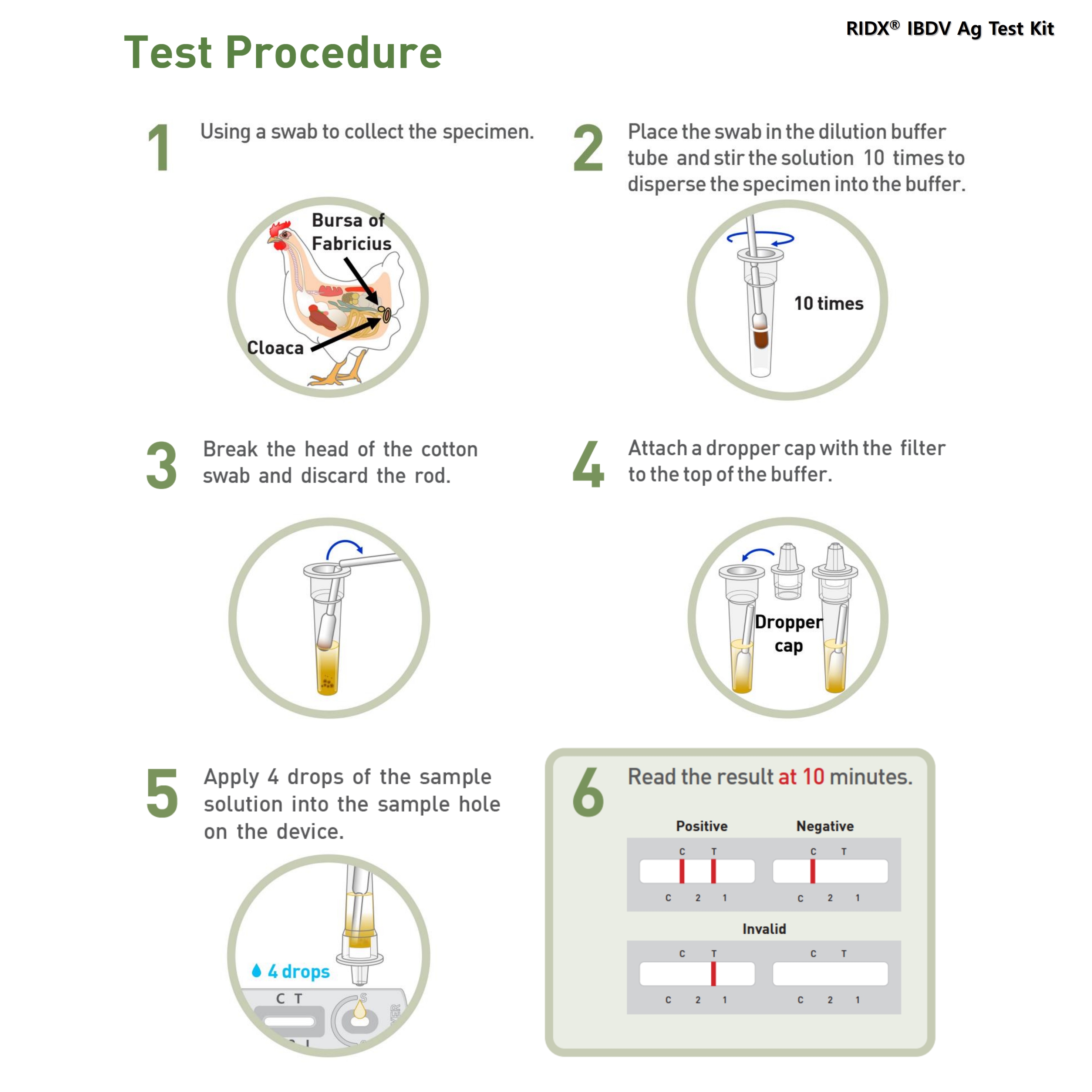
TEST PROCEDURE
1. All samples and test components should be at room temperature (15~30°C/59~86℉) before use.
2. Using a swab to collect specimen.
3. Put the swab into the sample dilution buffer tube and stir the solution 10 times with the swab to disperse the specimen into the buffer.
4. Break the head of the cotton swab and discard the rod.
5. Attach a dropper cap to the top of the buffer tube.
6. Apply 4 drops (approximately 100 μL) of the processed solution in the sample hole on the device.
7. Read test result at 10 minutes.